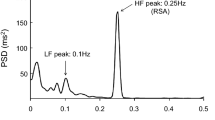
As we previously reported, resonant frequency heart rate variability biofeedback increases baroreflex gain and peak expiratory flow in healthy individuals and has positive effects in treatment of asthma patients. Biofeedback readily produces large oscillations in heart rate, blood pressure, vascular tone, and pulse amplitude via paced breathing at the specific natural resonant frequency of the cardiovascular system for each individual. This paper describes how resonance properties of the cardiovascular system mediate the effects of heart rate variability biofeedback. There is evidence that resonant oscillations can train autonomic reflexes to provide therapeutic effect. The paper is based on studies described in previous papers. Here, we discuss the origin of the resonance phenomenon, describe our procedure for determining an individual's resonant frequency, and report data from 32 adult asthma patients and 24 healthy adult subjects, showing a negative relationship between resonant frequency and height, and a lower resonant frequency in men than women, but no relationship between resonant frequency and age, weight, or presence of asthma. Resonant frequency remains constant across 10 sessions of biofeedback training. It appears to be related to blood volume.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Angelone, A., & Coulter, N. A. Jr. (1964). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: A frequency depended phenomenon. Journal of Applied Physiology, 19, 479–82.
Chernigovskaya, N. V., Vaschillo, E. G., Rusanovsky, B. B., & Kashkarova, O. E. (1990). Instrumental autotraining of mechanisms for cardiovascular function regulation in treatment of neurotics. The SS Korsakov's Journal of Neuropathology and Psychiatry, 90, 24–28.
Cooke, W. H., Cox, J. F., Diedrich, A. M., Taylor, J. A., Beightol, L. A., Ames, J. E. 4th, Hoag, J. B., Seidel, H., & Eckberg, D. L. (1998). Controlled breathing protocols probe human autonomic cardiovascular rhythms. American Journal of Physiology, 274(2 Pt 2), H709–18.
DeBoer, R. W., Karemaker, J. M., & Strackee, J. (1987). Hemodynamic fluctuations and baroreflex sensitivity in humans: A beat-to-beat model. American Journal of Physiology, 253 (Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 22), H680–H689.
Giardino, N., Lehrer, P. M., & Feldman, J. (2000). The role of oscillations in self-regulation: their contribution to homeostasis. In D. Kenney & F. J. McGuigan (Ed.), Stress and health: Research and clinical applications (pp. 27–52). Harwood Publishers.
Giardino, H. D., Glenny, R. W., Borson, S., & Chan, L. (2003). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia is associated with efficiency of pulmonary gas exchange in healthy humans. American Journal of Physiology (Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 284), H1585–H1591.
Giardino, N. D., Chan, L., & Borson, S. (2004). Combined heart rate variability and pulse oximetry biofeedback for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: preliminary findings. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 29, 121–133.
Grodins, F. S. (1963). Control theory and biological systems. New York: Columbia University Press.
Halamek, J., Kara, T., Jurak, P., Soucek, M., Francis, D. P., Davies, L. C., Shen, W. K., Coats, A. J., Novak, M., Novakova, Z., Panovsky, R., Toman, J., Sumbera, J., & Somers, V. K. (2003). Variability of phase shift between blood pressure and heart rate fluctuations: a marker of short-term circulation control. Circulation, 22,108(3), 292–307.
Hamilton, L. L., Lindan, O., & Reswick, J. B. (1969). Dynamic effects of sinusoidal tilting on heart rate of healthy and paralyzed persons. Journal of Applied Physiology, 27(3), 378–384.
Hammer, P. E., & Saul, J. P. (2005). Resonance in a mathematical model of baroreflex control: arterial blood pressure waves accompanying postural stress. American Journal of Physiology Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 288(6), R1637–1648.
Herbs, D., Gevirtz, R. N., & Jacobs, D. (1993). The effect of heart rate pattern biofeedback for the treatment of essential hypertension. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 19, 281 (abstract).
Hasset, A., Radvanski, D., & Lehrer, P. (2006). Heart rate variability biofeedback as a treatment for fibromyalgia. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the International Society for Advancement of Respiratory Psychophysiology, Princeton, NJ, October 17–19. Biological Psychology, 72, 232–233 (abstract).
Ito, T., Takamata, A., Yaegashi, K., Itoh, T., Yoshida, T., Kawabata, T., Kimura, M., & Morimoto, T. (2001). Role of blood volume in the age-associated decline in peak oxygen uptake in humans. Japanese Journal of Physiology, 51, 607–612.
Karavidas, M. (2005). Heart variability biofeedback in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 30(4), 397–423.
Karavidas, M., & Lehrer, P. (2006). A pilot study of heart rate variability (HRV) Biofeedback as a treatment for major depression. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the International Society for Advancement of Respiratory Psychophysiology, Princeton, NJ, October 17–19. Biological Psychology, 72, 234–235.
Legramante, J. M., Raimondi, G., Massaro, M., Cassarino, S., Peruzzi, G., & Iellamo, F. (1999). Investigating feed-forward neural regulation of circulation from analysis of spontaneous arterial pressure and heart rate fluctuations. Circulation, 99, 1760–1766.
Lehrer, P. M., Carr, R. E., Smetankine, A., Vaschillo, E., Peper, E., Porges, S., Edelberg, R., Hamer, R., & Hochron, S. (1997). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia vs neck/trapezius EMG and incentive inspirometry biofeedback for asthma: a pilot study. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 22, 95–109.
Lehrer, P. M., Vaschillo, E., & Vaschillo, B. (2000). Resonant frequency biofeedback training to increase cardiac variability: rationale and manual for training. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 25, 177–191.
Lehrer, P. M., Vaschillo, E., Vaschillo, B., Lu, S. E., Eckberg, D. L., Edelberg, R., Shih, W. J., Lin, Y., Kuusela, T. A., Tahvanainen, K. U. O., & Hamer, R. (2003). Heart rate variability biofeedback increases baroreflex gain and peak expiratory flow. Psychosomatic Medicine, 65, 796–805.
Lehrer, P., Vaschillo, E., Vaschillo, B., Lu, S., Scardella, A., Siddique, M., & Habib, R. (2004). Biofeedback Treatment for Asthma. Chest, 126, 352–361.
Lindqvist, A. (1990). Noninvasive methods to study autonomic nervous control of circulation. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica Supplementum, 588, 1–107.
London, G. M., Guerin, A. P., Laurent, S., London, A. M., & Safar, M. E. (1985). Cardiopulmonary blood volume and plasma renin activity in man: preliminary report. Journal of Hypertension-Supplement, 3, S121–S123.
McCraty, R., Atkinson, M., & Tomasino, D. (2003). Impact of a workplace stress reduction program on blood pressure and emotional health in hypertensive employees. The Journal of Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 9, 355–369.
Mier, C. M., Domenick, M. A., Turner, N. S., & Wilmore, J. H. (1996). Changes in stroke volume and maximal aerobic capacity with increased blood volume in men women. Journal of Applied Physiology, 80, 1180–1186.
Porges, S. W. (1995) Orienting in a defensive world: mammalian modifications of our evolutionary heritage. A polyvagal theory. Psychophysiology, 32, 301–318.
Radvanski, D., Vaschillo, E., Vaschillo, B., Hassett, A., Lehrer, P., & Sigal, L. (2004) Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback for Fibromyalgia Treatment. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 29, 308.
Ringwood, J. V., & Malpas, S. C. (2001). Slow oscillations in blood pressure via a nonlinear feedback model. American Journal of Physiology. Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 280(4), R1105–R1115.
Saul, J. P., Berger, R. D., Albrecht, P., Stein, S. P., Chen, M. H., Cohen, R. J. (1991). Transfer function analysis of the circulation: unique insights into cardiovascular regulation. American Journal of Physiology, 261(4 Pt 2), H1231–1245.
Shevde, K., Pagala, M., Tyagaraj, C., Udeh, C., Punjala, M., Arora, S., & Elfaham, A. (2002). Preoperative blood volume deficit influences blood transfusion requirements in females and males undergoing coronary bypass graft surgery. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia, 14, 512–517.
Sleight, P., La Rovere, M., Mortara, A., Pinna, G., Maestri, R., Leuzzi, S., Bianchini, B., Tavazzi, L., & Bernardi, L. (1995). Physiology and pathophysiology of heart rate and blood pressure variability in humans: is power spectral analysis largely an index of baroreflex gain? Clinical Science, 88, 103–109.
Tiedt, N., Wohlgemuth, B., & Wohlgemuth, P. (1975). Dynamic characteristics of heart-rate responses to sine-function work-load patterns in man. Pflugers Archiv, 355(2), 175–187.
Ursino, M., & Magosso, E. (2003). Role of short-term cardiovascular regulation in heart period variability: a modeling study. American Journal of Physiology—Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 284, H1479–H1493.
Vashchillo, E. G., Zingerman, A. M., Konstantinov, M. A., & Menitsky, D. N. (1983) Research of the resonance characteristics for cardiovascular system. Human Physiology, 9, 257–265.
Vaschillo, E. G. (1984). Dynamics of slow-wave cardiac rhythm structure as an index of functional state of an operant. Unpublished Doctoral dissertation. Saint Petersburg, Russia: Institute of Experimental Medicine.
Vaschillo, E., Lehrer, P., Rishe, N., & Konstantinov, M. (2002). Heart rate variability biofeedback as a method for assessing baroreflex function: a preliminary study of resonance in the cardiovascular system. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 27, 1–27.
Vaschillo, E., Vaschillo, B., & Lehrer, P. (2004). Heartbeat synchronizes with respiratory rhythm only under specific circumstances. Chest, 126(4), 1385–1406.
Vaschillo, E., Vaschillo, B., Lehrer, P., Bates, M. E., Ray, S., Udo, T., & Pandina, R. (2005). Using Heart Rate Variability to evaluate response to drug-related stimuli: A new approach. Psychophysiology, 42, Suppl. 1, 125.
Vaschillo, E., Vaschillo, B., Bates, M. E., Lehrer, P., Pandina, R., Ray, S., & Udo, T. (2005). Heart rate resonance features do not depend on respiration. Biological Psychology, in press.
Wigertz, O. (1971). Dynamics of respiratory and circulatory adaptation to muscular exercise in man. A systems analysis approach. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica Supplementum, 363, 1–32.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant #R01 HL58805 from the Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health and by Grant # R01 AA0 15248–01 from NIDA and NIAAA. The authors are indebted to Dwain Eckberg for his assistance in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaschillo, E.G., Vaschillo, B. & Lehrer, P.M. Characteristics of Resonance in Heart Rate Variability Stimulated by Biofeedback. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 31, 129–142 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-006-9009-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-006-9009-3